Call: 08045814144
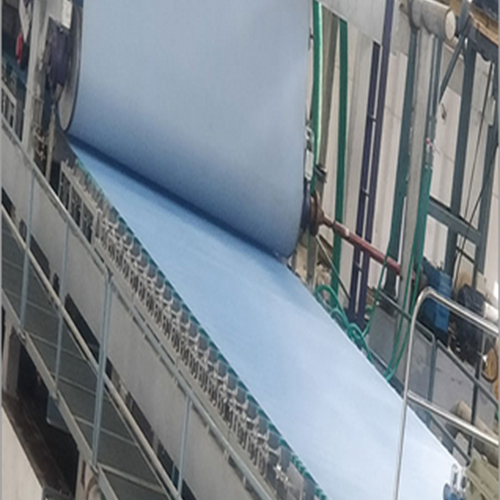
Single Wire Paper Machine

Product Details:
- Grade Semi-Automatic
- Material SS
- Computerized Yes
- Control System PLC Control
- Voltage 220-440 Volt (v)
- Color Mid Green
- Warranty 1 Year
30000000.0 INR/Unit
X
Single Wire Paper Machine Price And Quantity
- 1 Unit
- 30000000.0 INR/Unit
Single Wire Paper Machine Product Specifications
- PLC Control
- 1 Year
- 220-440 Volt (v)
- Mid Green
- Semi-Automatic
- Yes
- SS
Single Wire Paper Machine Trade Information
- INDIA
- Cash in Advance (CID) Cash Advance (CA)
- 2 Unit Per Year
- 6 Months
- Yes
- Standard Packing
- Asia North America South America Eastern Europe Middle East Africa Australia Central America Western Europe
- All India
- ISO , IEC,
Product Description
GSm Range:- 40 To 180Production Capacity:- up To 400 Ton
Product:- News Print Paper, Writing & Printing Paper,Craft Paper
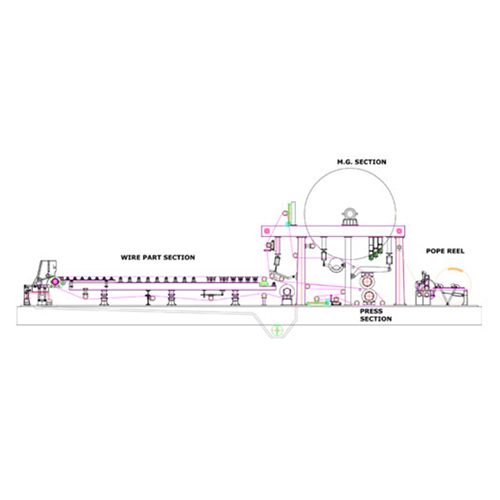
Key Components and Operation:
- Headbox: The process begins with the headbox, which evenly distributes the pulp slurry (a mixture of fibers and water) across the width of the wire. The headbox is designed to ensure a consistent flow and fiber dispersion onto the forming wire.
- Forming Section (Wet End):
- Single Forming Wire: This is the defining characteristic. A continuous loop of finely woven mesh (historically metal, now often synthetic polymers) moves continuously.
- Dewatering: The pulp slurry from the headbox is deposited onto this moving wire. As the wire travels, water drains through the mesh due to gravity, vacuum (from suction boxes located beneath the wire), and the movement itself. This leaves a mat of fibers on the wire, forming the wet paper web.
- Supporting Elements: The forming section includes various rolls (like the breast roll and couch roll), foils, and suction boxes that support the wire and aid in water removal and sheet formation. Sometimes a dandy roll is used on top of the wet web to improve surface finish.
- Press Section: The fragile, wet paper web is then transferred from the forming wire to a series of presses. These consist of rollers (often covered with felt) that apply pressure to squeeze out more water from the sheet, further compacting the fibers and increasing the web's strength.
- Drying Section: The partially dried paper web travels through a series of heated cylinders. These cylinders are typically steam-heated and evaporate the remaining water in the sheet, bringing the moisture content down to the desired level. Sometimes infrared dryers are used to supplement the cylinder drying.
- Size Press (Optional): In some machines, after partial drying, the paper sheet passes through a size press where starch or other chemicals are applied to improve surface properties like strength, water resistance, and printability.
- Calender Section: The dried (or sized) paper then goes through a calender stack, which consists of a series of smooth rollers. These rollers smooth the surface of the paper and control its thickness and finish (e.g., smoothness or gloss).
- Reel Section: Finally, the finished paper web is wound onto large rolls at the reel section, ready for further processing (converting, cutting, etc.).
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry